 ‘ );
‘ );
h3_html = ‘
‘+cat_head_params.sponsor.headline+’
‘;
cta = ‘‘+cat_head_params.cta_text.text+’→‘
atext = ‘
‘+cat_head_params.sponsor_text+’
‘;
scdetails = scheader.getElementsByClassName( ‘scdetails’ );
sappendHtml( scdetails[0], h3_html );
sappendHtml( scdetails[0], atext );
sappendHtml( scdetails[0], cta );
// logo
sappendHtml( scheader, ” );
sc_logo = scheader.getElementsByClassName( ‘sc-logo’ );
logo_html = ”;
sappendHtml( sc_logo[0], logo_html );
sappendHtml( scheader, ” );
if(“undefined”!=typeof __gaTracker){
__gaTracker(‘create’, ‘UA-1465708-12’, ‘auto’, ‘tkTracker’);
__gaTracker(‘tkTracker.set’, ‘dimension1’, window.location.href );
__gaTracker(‘tkTracker.set’, ‘dimension2’, ‘seo’ );
__gaTracker(‘tkTracker.set’, ‘contentGroup1’, ‘seo’ );
__gaTracker(‘tkTracker.send’, { ‘hitType’: ‘pageview’, ‘page’: cat_head_params.logo_url, ‘title’: cat_head_params.sponsor.headline, ‘sessionControl’: ‘start’ });
slinks = scheader.getElementsByTagName( “a” );
sadd_event( slinks, ‘click’, spons_track );
}
} // endif cat_head_params.sponsor_logo
Google has published a new developer document that goes over the basics of JavaScript SEO.
The guide was written by Google’s Martin Splitt and Lizzi Harvey. Splitt has become an authority on JavaScript SEO, having recently produced a video series on the subject.
The guide goes over much of what was covered in the video series and focuses on getting JavaScript content indexed by Google.
As stated, it’s the literal basics. There’s nothing more basic to SEO than getting content indexed by Google.
Here’s a brief summary of the information included in the guide.
What’s in the Guide
The guide starts off by describing the three-step process of processing JavaScript content – crawling, rendering, indexing.
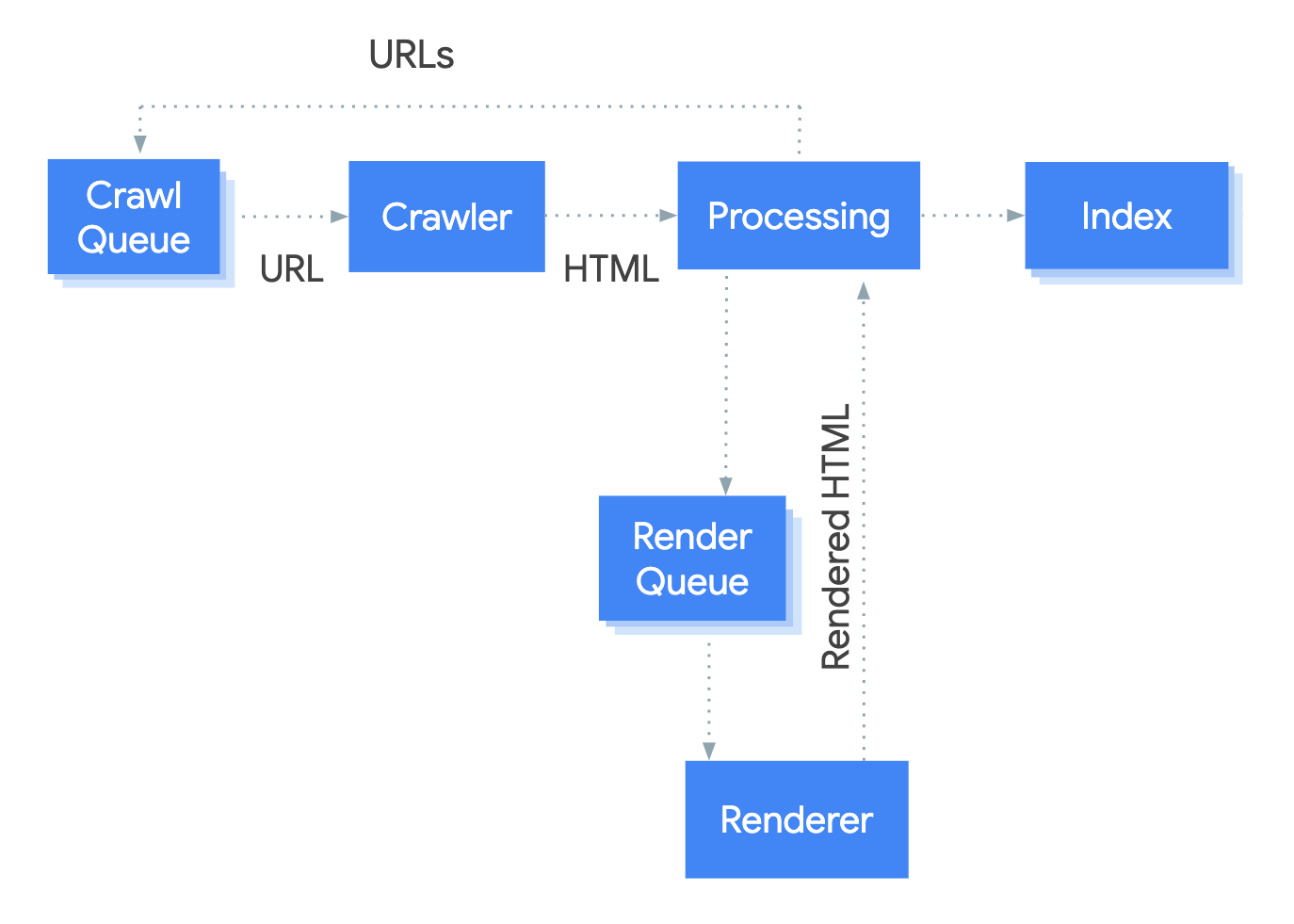
Then the guide goes over a few simple tips for making JavaScript content Google-friendly.
Those tips include:
- Unique titles and snippets: JavaScript can be used to change the meta description and the title.
- Write compatible code: To make sure your code is compatible with Googlebot, follow Google’s guidelines for troubleshooting JavaScript problems.
- HTTP status codes: Use a meaningful status code to tell Googlebot if a page should not be crawled or indexed, or whether a page has been moved to a new URL.
- Use meta robots tags carefully: Google warns using JavaScript to change the robots meta tag might not work as expected. If you want to use JavaScript to change the content of the robots meta tag, do not set the meta tag’s value to “noindex”.
- Lazy-loading: To save on bandwidth and improve performance, use lazy-loading to only load images when the user is about to see them.
Read the full guide here.
